CBT is a skills-based, present-focused, and goal-oriented treatment approach that targets the thinking styles and behavioral patterns that cause and maintain depression-like behavior and mood. Depression in adults is commonly associated with thinking styles that are unrealistically negative, self-focused and critical, and hopeless in nature. Ruminative thinking processes are also typical. Cognitive skills are used to identify the typical “thinking traps” (cognitive distortions) that clients engage in and treatment aims at getting the client to commit to and consider the evidence more fairly. Depressed adults also demonstrate increased isolation, withdrawal, simultaneous rejection of others and sensitivity to rejection, and decreased activity and enjoyment in activities. They typically experience a number of functional impairments including disrupted sleep cycles, eating and appetite issues, and increased thoughts of death and dying. Behavioral interventions can often help these interpersonal and functional impairments. Behavioral interventions include problem solving, behavioral activation, and graded activation or exposure. Treatment is generally time-limited and can be conducted in individual or group formats.
Program Goals:
The goals of CBT are to help clients:
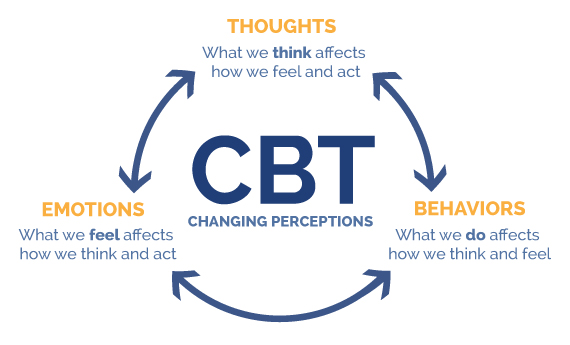
- Distinguish between thoughts and feelings.
- Become aware of how their thoughts influence feelings in ways that are not helpful.
- Evaluate critically the veracity of their automatic thoughts and assumptions.
- Develop the skills to notice, interrupt, and intervene at the level of automatic thoughts.
- Use behavioral techniques to identify situations that trigger distress and sadness.
- Use behavioral activation to become more attuned with meaningful reinforcement in their lives.
- Develop active problem-solving skills.














